As knowledge and understanding of the climate crisis continue to spread, consumers are gravitating toward actions that can reduce their carbon footprints. According to a 2021 study by the Pew Research Center, 80% of people are willing to change their lifestyle and how they work to lessen the effects of climate change. These actions include choosing the products they purchase and consume.
Businesses, thus, treat climate concerns and customer purchasing patterns as an incentive to figure out how to make their products and services more sustainable. This is where the value of biodegradable packaging comes in.
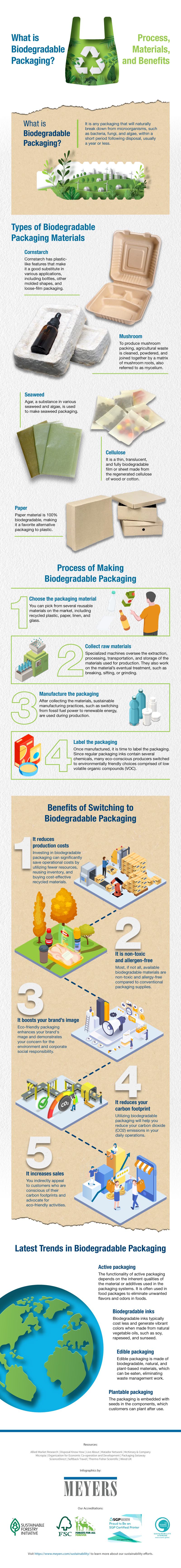
The Ins and Outs of Biodegradable Packaging
What is it?
Biodegradable means a material can break down naturally into smaller components as organisms and microorganisms—bacteria, fungi, algae, etc.—come into contact with them. Generally, biodegradable items decompose within a year or less and do not cause pollution.
Based on these definitions, one can easily conclude that some kinds of plastic do not fit the bill, as they can take hundreds of years to decompose. Here, the usual suspects include plastic bags and bottles.
According to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), the packaging boxes industry uses 36% of all plastic production, including single-use food and beverage containers.
Biodegradable packaging can be an excellent alternative to traditional ones that may harm the environment and its ecosystems.
Types of Biodegradable Packaging
The types of biodegradable packaging differ based on the material used and their purpose. Here are some examples.
- Recycled packaging
This packaging comprises materials used, cleaned, and repurposed as a new product. Recycled packaging helps reduce waste in dumps or landfills, which store waste but take years to decompose the accumulated garbage.
- Edible packaging
Edible packaging is usually plant- or fungus-based, so it is safe to eat. Besides using zero-waste materials, this packaging can enhance the flavors of the food it contains and provide an easy source of nutrients on the go.
- Plantable packaging
You’ll often see this packaging in industries that manufacture jewelry and cosmetics. These products use this packaging as fillers or wraps to protect the items during shipping. Once consumers no longer need the packaging, they can take the seeds from the packaging and plant them to grow healthy green foliage.
So while most, if not all, biodegradable packaging is safe to dispose of in the ground, plantable packaging goes a step further by letting discarded materials bloom into plants that help the environment and beautify surrounding areas.
- Biodegradable inks
The inks used in traditional packaging are usually petroleum-based and release volatile organic compounds as they degrade. By contrast, biodegradable ink contains little to no harmful substances and is generally cheaper than non-biodegradable ones.
Get Behind Biodegradable Packaging
More and more innovations find their way into the biodegradable packaging industry. From making sustainable alternatives cheaper and more efficient to enabling brands to produce unique packaging designs, there’s an opportunity for your company to adopt more eco-friendly packaging ideas.
If you want to learn more, the infographic below discusses everything you need to know about biodegradable packaging: its nature, types, and benefits for your business.